The Prompt Report: A systematic Survey of Prompting Techniques
Unveiling the Depths of Prompting in Large Language Models
Most people just scratch the surface of prompting when they interact with Large Language Models (LLMs). If you’ve ever wondered what prompting techniques exist out there, the paper “𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗺𝗽𝘁 𝗥𝗲𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁: 𝗔 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝗦𝘂𝗿𝘃𝗲𝘆 𝗼𝗳 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗺𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗧𝗲𝗰𝗵𝗻𝗶𝗾𝘂𝗲𝘀“ is a goldmine of insights.

Understanding Prompting
Prompting influences how LLMs respond. By crafting prompts carefully, you can guide the models to perform various tasks, from creative writing to data analysis. This paper delves into the world of prompting, explaining the basics and showing how users can make the most of LLMs in flexible and personalized ways. It also covers advanced techniques like prompt design and engineering, exploring applications in fields such as medicine and keyphrase extraction.
It has an associated github here:
https://github.com/trigaten/The_Prompt_Report
𝗘𝘅𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗖𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗮𝗴𝗲
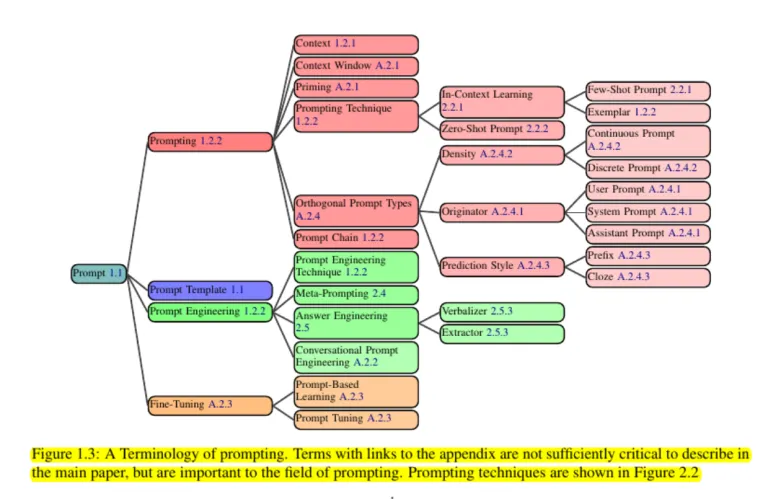
- 33 Vocabulary Terms: Essential terminology for understanding prompting.
- 58 Text-Only Prompting Techniques: Detailed techniques specifically for text-based tasks.
- 40 Techniques for Other Modalities: Prompting methods for image, audio, video, segmentation, and 3D prompting.
- In-Depth Analysis: Focuses on discrete prefix prompts, widely used with modern LLM architectures.
- Multilingual Techniques: The taxonomy extends beyond English text, covering multilingual techniques like translate-first prompting and cross-lingual in-context learning (ICL).
- Advanced Applications: Explores complex techniques involving agents that access external tools, code generation, and retrieval-augmented generation.
- Evaluation and Security: Discusses various evaluation methods and highlights important issues such as security (prompt hacking), overconfidence, biases, and ambiguity.
Key Prompting Techniques Identified
- In-Context Learning (ICL): Learning from exemplars/instructions within the prompt.
- Zero-Shot Prompting: Prompting without examples.
- Thought Generation: Encouraging the LLM to articulate its reasoning.
- Decomposition: Breaking down complex problems into simpler sub-questions.
- Ensembling: Using multiple prompts and aggregating outputs.
- Self-Criticism: Having the LLM critique its own outputs to improve performance.
A Full Course on Prompting
This paper is like a full course on prompting, offering invaluable insights and practical techniques for anyone looking to master the art of interacting with LLMs.
Access the Full Report
The Prompt Report is here, for you to read. The Prompt Report: A Systematic Survey of Prompting Techniques

For a more detailed exploration, you can access the full report on GitHub:
This paper helps you gain a deeper understanding of how to harness the full potential of LLMs, improving your ability to use these models effectively in various applications.