P.R.O.M.P.T.S Framework : Advanced Prompting to Unlock the Power of LLMs
Ever feel like you're talking to a wall when you ask your AI a simple question and end up with a generic answer that adds no real value? If you've only ever tried quick one-liner prompts like “What is climate change?” or “Tell me about electric cars” and received vague, unsatisfying responses, you’re not alone.
Many newcomers discover that basic prompting often results in answers that don’t tap into the full potential of these powerful models.
In "PROMPTCraft—Making AI Dance to Your Tunes” classes—we show you how to get the most out of AI by crafting better prompts. It isn’t magic—it’s all in the prompt.
Let us introduce the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework, an advanced, structured approach that ensures your prompts are clear, comprehensive, and designed to deliver exceptional results.
What Is the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework?
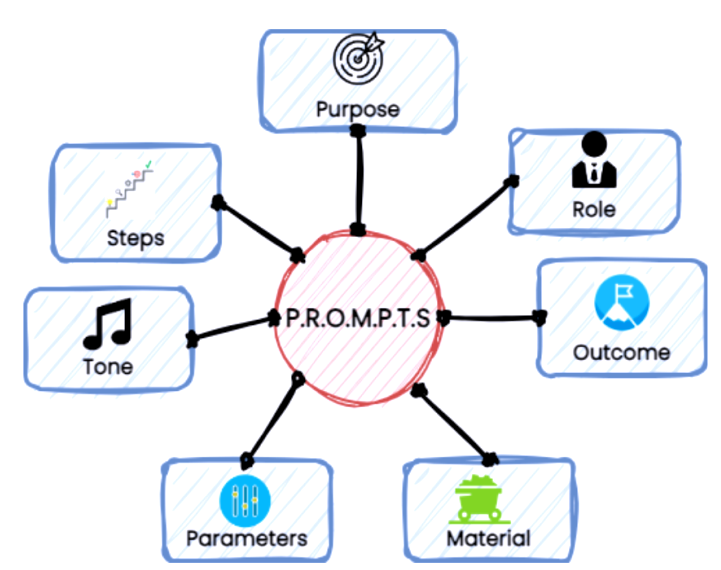
The P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework is an acronym that stands for:
- Purpose
- Role
- Outcome
- Material
- Parameters
- Tone
- Steps
These elements play a crucial role in constructing a prompt that guides the LLM effectively. By breaking down your instructions into these components, you create a roadmap that the model can follow to generate precise and actionable outputs. Lets break these components down and see how they guide LLMs to an optimal response early and frequently.
The Components of P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework
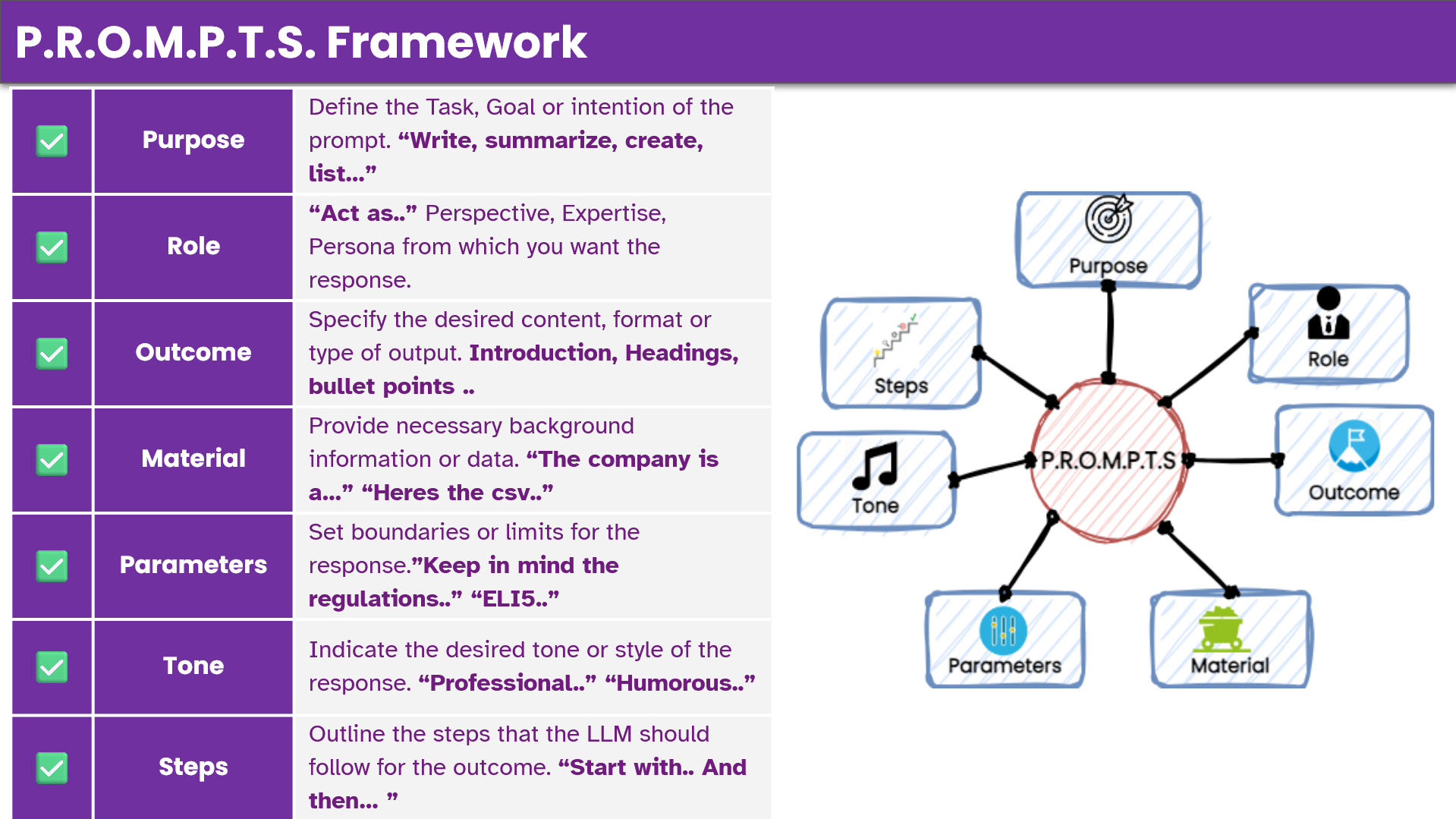
1. Purpose
Definition: Clearly state what you want the LLM to do.
Examples:
- “Write an article…”
- “Summarize this report…”
- “Create a list of…”
Why It Matters:
A defined purpose sets the task's direction. The model immediately understands whether it’s expected to generate creative content, summarize data, or compile a list, thereby reducing ambiguity.
2. Role
Definition: Assign a role or persona to the model.
Examples:
- “Act as an experienced Chief Marketing Officer…”
- “Imagine you are a renowned data scientist…”
Why It Matters:
Specifying a role infuses the response with a particular perspective or expertise. This alignment ensures that the output reflects the appropriate tone and level of detail.
3. Outcome
Definition: Define the desired format and structure of the response.
Examples:
- “Provide a comprehensive marketing plan in markdown format…”
- “Generate bullet points summarizing the key ideas…”
Why It Matters:
A clear outcome tells the LLM exactly what to produce, whether it’s an essay, a report with headings, a list, or a step-by-step guide. This helps the model to format its answer as required.
4. Material
Definition: this is where you provide whatever your context is. Supply any necessary background information or data.
Examples:
- “The company is a market leader in eco-friendly products…”
- “Here’s the csv data of last year’s sales…”
Why It Matters:
Providing context enables the model to ground its response in relevant information. Material can be specific facts, datasets, or background narratives that enrich the final output.
5. Parameters
Definition: Set boundaries or specific constraints for the response.
Examples:
- “Keep the language concise and use short, punchy sentences…”
- “Focus only on first-time car buyers in six major Indian cities…”
Why It Matters:
Parameters guide the model by outlining the scope and limitations of the task. They help prevent drift into irrelevant details and ensure compliance with specific requirements like tone, style, or content restrictions.
6. Tone
Definition: Indicate the desired tone or style of the output.
Examples:
- “Professional and engaging…”
- “Conversational yet authoritative…”
Why It Matters:
Tone is essential for ensuring that the response resonates with the intended audience. Whether it’s formal, casual, humorous, or inspiring, the tone sets the mood and influences word choice and structure.
7. Steps
Definition: Outline the sequence of actions or logical flow the model should follow.
Examples:
- “Start by identifying the target audience, then research competitors, and finally develop key messaging points…”
Why It Matters:
Providing clear steps helps the LLM break down complex tasks into manageable parts. This sequential approach minimizes errors and enhances clarity in the final output.
Why This Technique Works
- Clarity and Structure: Breaking the prompt into discrete components minimizes ambiguity.
- Role Alignment: Assigning a role ensures that the output is contextually relevant and expert-driven.
- Tailored Outcomes: Specifying the desired format and tone leads to more usable and audience-appropriate responses.
- Step-by-Step Guidance: Outlining steps helps the LLM logically work through complex tasks.
This method not only increases the precision of the generated content but also empowers you to anticipate and solve potential issues before they arise.
Lets take some examples
Example 1: Meal Planning
The ask
Think for a minute about what you need when you ask for a meal plan? You want to create a weekly meal plan that is healthy, budget-friendly, and easy to prepare for every meal of the day.
- You want ideas that a friendly meal-planning coach or kitchen helper would suggest.
- You would prefer a list or table that shows meals for each day of the week, along with a brief recipe for each meal.
- You prefer recipes using common ingredients found at home. Also you prefer Indian style food.
- the plan should be one week, three meals per day, and focus on health and affordability.
- You don't want complex strategies, you just want friendly and easy to understand plan, much like advice from a trusted family member.
Structuring the prompt
Lets transform this into a structured prompt using the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. framework.
- P – Purpose: “I need a weekly meal plan that is healthy and cost-effective, with simple recipes for breakfast, lunch, and dinner.”
- R – Role: “Act as a friendly meal planning coach who offers simple, everyday recipes.”
- O – Outcome: “Provide a clear, easy-to-read meal plan for the week that includes breakfast, lunch, and dinner for each day, plus a short recipe description for each meal.”
- M – Material: “Use ingredients that are common in a typical Indian home kitchen, so no special items are needed.”
- P – Parameters: The plan should cover 7 days. Each day must include suggestions for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The recipes should be quick, healthy, and budget-friendly. The recipe should be based on Indian style home kitchen.
- T – Tone: “Use a friendly, conversational tone that’s easy to follow. Ask questions where you need more information”
- S – Steps: "List each day of the week (Monday through Sunday). For each day, suggest a simple recipe for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Include a one- or two-sentence description of each recipe and list the basic ingredients needed."
Putting It All Together
Once you have thought through what you need, this is what your final prompt may look like.
I need help planning meals for the week. Please act as a friendly meal planning coach and create a weekly meal plan that is healthy, budget-friendly, and easy to prepare. I’d like the plan to cover all 7 days (Monday to Sunday) and include suggestions for breakfast, lunch, and dinner each day. For every meal, please provide a simple recipe description and list the basic ingredients needed—make sure to use common items found in a regular Indian home kitchen. Use a friendly, conversational tone that’s easy to follow.
Example 2: Email for a dinner party
The Ask
Take a moment to think about what you need when you ask for an email draft. You want an email that’s friendly and informal—a warm invitation to a dinner party next weekend. You’d like it to sound just like a note from a close friend, including all the essential details like the date, time, and location, and ending with a casual request for an RSVP.
Structuring the Prompt Using the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework
- P – Purpose: “I need a friendly, informal email invitation for a dinner party next weekend.”
- R – Role: “Act as a warm, friendly friend who loves hosting gatherings.”
- O – Outcome: “Provide a clear and casual email draft that invites a friend to a dinner party. The email should include key details like the date, time, and location, and should feel personal and inviting.”
- M – Material: “Mention that the dinner party is at my home next weekend. Feel free to add any casual details that make the invitation more personal.”
- P – Parameters: “The email should be informal and friendly, not too long, and must clearly mention that the dinner party is next weekend with the essential details like time and location.”
- T – Tone:“Use a casual, warm, conversational tone—just like a message from one friend to another.”
- S – Steps:“Start with a friendly greeting, mention the dinner party invitation, provide the details (date, time, location), add a note asking for an RSVP, and finish with a warm closing.”
Putting It All Together
Once you’ve thought through what you need, your final prompt might look like this:
"I need help drafting a friendly, informal email inviting a friend to a dinner party next weekend. Please act as a warm, casual friend who loves hosting gatherings. Create an email that starts with a friendly greeting, states the invitation to a dinner party at my house next weekend, and includes the essential details like the date, time, and location. Also, please add a note asking if they can join and finish with a warm, personal closing. Use a casual, conversational tone that sounds genuine—just like a note from one friend to another. "
Example 3: Travel Itinerary to Jaipur, India.
The Ask
Take a moment to think about what you need when planning a travel itinerary. You want to create a detailed two-day plan for a weekend trip to Jaipur, India. You’d like an itinerary that covers popular attractions, tasty dining options, and free or budget-friendly activities to make the most of your short getaway. The plan should be easy to follow and provide practical suggestions so you can experience the best of Jaipur without any hassle.
Structuring the Prompt Using the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework
- P – Purpose: “I need a two-day itinerary for a weekend trip to Jaipur, India, that includes popular attractions, dining options, and free activities.”
- R – Role: “Act as a travel guide who is familiar with Jaipur and its highlights.”
- O – Outcome: “Provide a day-by-day travel itinerary for a two-day trip to Jaipur. The itinerary should outline the key attractions, recommended places to eat, and suggestions for free or low-cost activities.”
- M – Material: “Use insights about Jaipur’s must-see landmarks, local dining favorites, and free activities that are popular with visitors.”
- P – Parameters: “The itinerary should cover two full days (a weekend trip) and include a morning, afternoon, and evening plan for each day. It should be concise yet informative, focusing on both well-known attractions and budget-friendly options.”
- T – Tone: “Use an informative and friendly tone, as if you’re offering travel advice to a friend planning a trip.”
- S – Steps:
“1. Divide the itinerary into Day 1 and Day 2.
2. For each day, suggest activities for the morning, afternoon, and evening.
3. Include brief descriptions of each activity along with any relevant tips such as best times to visit, nearby dining options, or transportation advice.”
Putting It All Together
Once you’ve thought through what you need, your final prompt might look like this:
"I need help planning a two-day itinerary for a weekend trip to Jaipur, India. Please act as a knowledgeable travel guide who is familiar with the city. Create a detailed, day-by-day itinerary that covers two days in Jaipur, including suggestions for popular attractions, local dining options, and free or budget-friendly activities. For each day, provide a plan for the morning, afternoon, and evening with brief descriptions and any useful tips like the best time to visit or nearby eateries. Use an informative and friendly tone, as if you’re giving travel advice to a friend planning their trip. "
So What does it all mean?
Now you know how to turn everyday requests into effective prompts using the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework. Instead of using generic one-line prompts that yield vague answers, this framework breaks your request into clear, structured parts so the AI understands exactly what you need.
By structuring your prompts with the P.R.O.M.P.T.S. Framework, you can turn simple queries into detailed, actionable instructions that get the most out of your interactions with AI. Whether you’re a busy mom, a school kid, or anyone new to LLMs, this approach helps ensure you receive thoughtful, well-organized responses that truly meet your needs.
This guide allows you to experiment with and master effective prompting techniques—unlocking the full potential of your AI for everyday tasks.
Happy prompting!